
Data Fetching - Explained Practically with NextJS
Read 233 times
#nextjs
#react
#fetch
SSG SSR and ISR. Letters that we’ve come across at some point in time. They only succeed in confusing me. Let’s see if I can make them clearer…
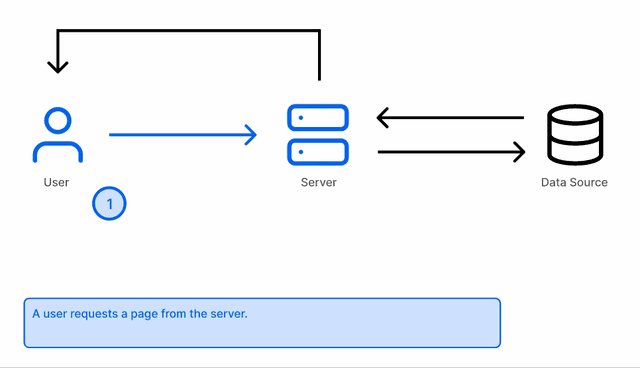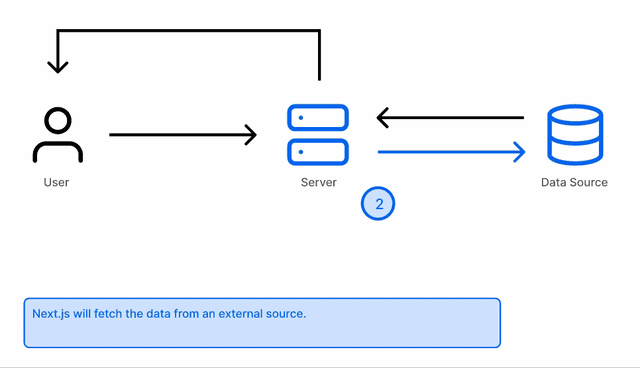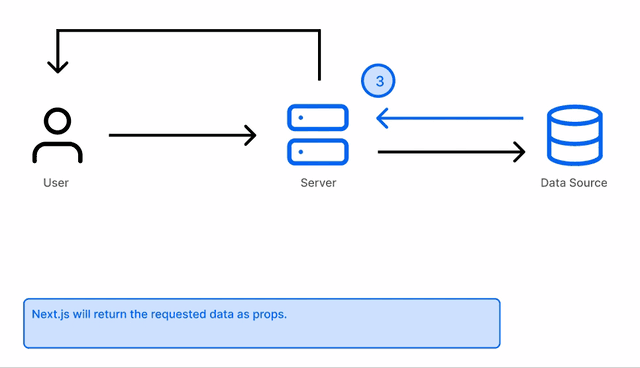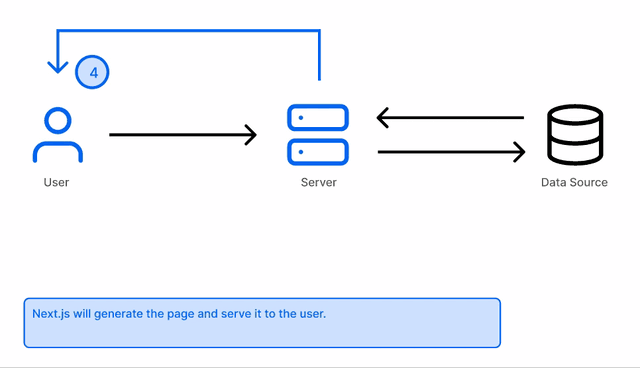
If you work in any frontend framework you are most likely going to be fetching data to display on your pages. Fetching it from a server, a headless cms or any other source you would pull data from.
In any of those instances, how you choose to fetch that data usually depends on how frequently that data changes and how soon those changes need to be shown on your frontend.
The issue I encounter with these abbreviations - these letters - is that I end up being more confused than I was before I began.
So I am going to try to explain these concepts practically with examples for my own sake. Explain them, so I can better conceptualise what’s going on.
I will be using NextJS as a basis for my explanations
There are usually two main scenarios when it comes to how you want your data fetched and rendered.
1. If you have a site like an eCommerce store - that data needs to be updated frequently.
Because your site data has to be updated often, you would most likely use this function:
export async function getServerSideProps(context){
const res = await fetch(`https://...`)
const data = await res.json()
return {
props {}
}
}
With getServerSideProps, the data is fetched and rendered on each request - this takes place at the server. It is Server Side Rendered. I don’t fully understand how that happens, so I won’t try to explain it any further.
2. If you had a site with static data - like a blog.
In this case, the data is rendered at build time instead and usually consists of two functions working in tandem:
- getStaticProps
- getStaticPaths
At build time, getStaticProps fetches all the data and serves it to your frontend using this function:
export async function getStaticProps(){
const res = await fetch(`https://...`)
const data = await res.json()
return {
props { data }
}
}
If the page is visited again, the static page that has already been rendered will be served. No additional call will be made
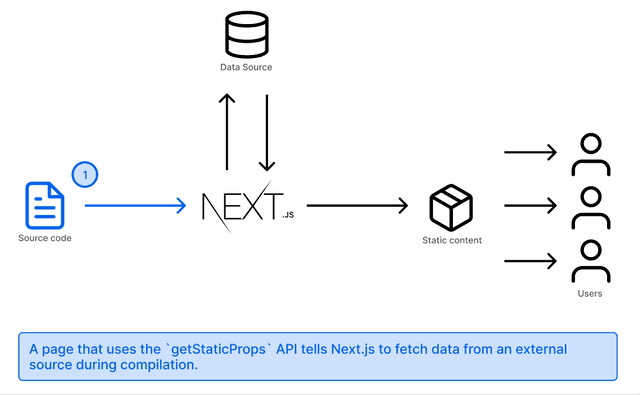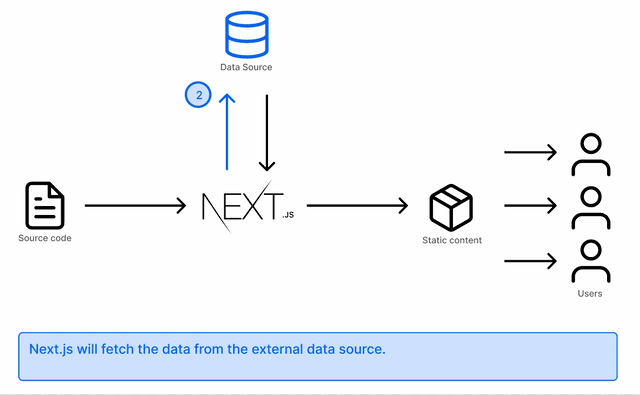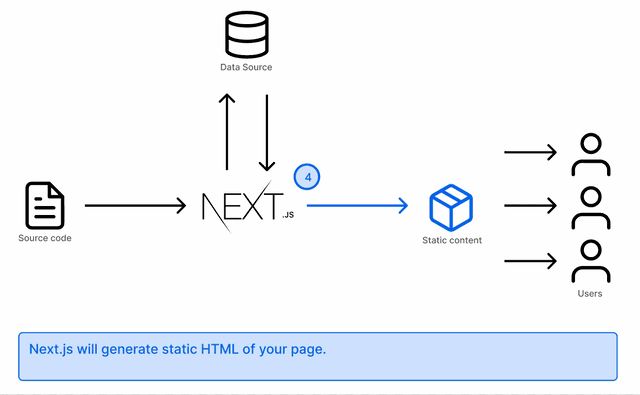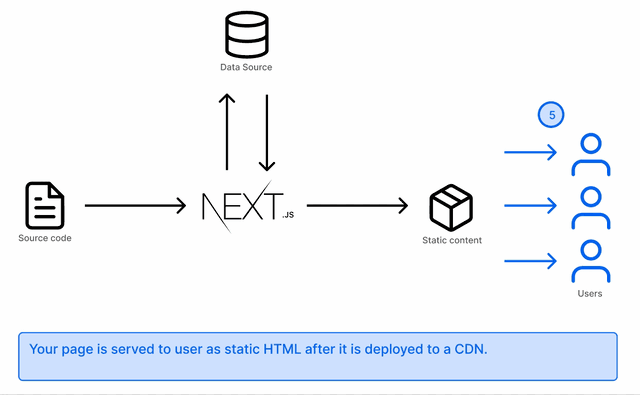
Your blog will most likely have a detail page of each post. That is achieved by using getStaticPaths to fetch the individual paths and render the pages matching them:
export async function getStaticPaths() {
return {
paths: [
{ params: { ... } }
],
fallback: false,
};
}
getStaticPaths fetches the paths(slugs) for all the pages you want to be made so Next knows how many pages it has to build and what content should be in each. The params from getStaticPaths are passed to getStatcProps to build the individual pages.
NOTE: It is also possible to use getStaticPaths with getServerSideProps
The Problems
While getStaticProps and get getStaticPaths used in this way, work well for your static site they are not without their issues.
There are two main problems we encounter with using these two functions in this way:
- Page content does not show updates or changes
- New pages made after the others have been built are not handled.
Let’s take a close look at these problems and how we can alleviate them.
Problem: Page Content Does Not Update
With the way demonstrated to write getStaticProps, if any of the existing content is changed or updated, nothing happens. Because the pages have already been built, any modifications will not reflect or render.
Solution: revalidate
To solve this, we would make an addition to the return statement of getStaticProps:
export async function getStaticProps(){
return {
props: data,
revalidate: 1
}
}
revalidate tells Next to wait a set number of seconds before regenerating the page content. This way, if we do make changes, they will be rendered. Keeping our site up to date.
Gotcha: revalidate works on a page by page basis and only for pages that already exist.
Problem: New Pages Are Not Handled
Let’s zoom in to the return statement of getStaticPaths specifically to the fallback parameter:
return {
paths: [
{ params: { ... } }
],
fallback: false,
};
fallback - which is required for this function - can be set to either false, true or blocking. But what do those mean?
False:
- If you visit a path that does not exist (not generated at first build), a 404 page will be shown.
- New pages are not generated.
True:
- If you visit a path that does not exist, Next will try and generate that page in the background. If it is successful, it will inject that data onto the page.
Blocking is beyond the scope of what I am trying to explain here - I just not in the mood for more confusion. Here are the docs
Solution: Set fallback to true
To solve the issue of new pages we would do this in our getStaticPaths:
export async function getStaticPaths() {
return {
paths: [
{ params: { ... } }
],
fallback: true,
};
}
By setting fallback to true, we ensure that any new pages we make are rendered and a visitor is not met with a 404 page unless that page truly doesn’t exist.
Gotcha: Whilst Next is trying to generate the new page, nothing is being shown onscreen. To avoid your visitor thinking that nothing is happening, add a skeleton page - as a placeholder - at the top of your page render:
export default function PostDetails({ post }) {
if (!post) return <Skeleton />
}
An additional catch will need to be implemented if the page truly doesn’t exist - a redirect to another place on the site or a custom 404 page.
Conclusion
This article has been an effort to simplify the abbreviations associated with data fetching. Using what I have covered I’ll end by saying this
- SSR - Server-Side Rendering: What
getServerSidePropsdoes. - SSG - Static Site Generation: What
getStaticPropsdoes by default. - ISR - Incremental Static Regeneration: What happens when you set
fallbacktotrueingetStatcPaths.
This article was originally published on Dante Decodes
Image Credit: Peter Mekhaeil
Thank you for reading, let’s connect!
Thank you for visiting this little corner of mine. Let’s connect on Twitter and LinkedIn